Multi-Model Comparison: The Future of AI Post-Editing

O.Translator
Mar 20, 2025

2. The Necessity of Post-Editing
3. Display of Translation Effects
-
3.1 Comprehensive Application of the Entire Document Context
-
3.2 Multi-Model Comparison to Select the Optimal Translation
1. Introduction
In the era of globalization and digitalization, document translation requires not only accurate language conversion but also the conveyance of the original text's context and essence. Traditional post-editing often encounters issues such as omissions, inconsistencies, and contextual deviations, which limit the effectiveness of cross-language communication.
With the assistance of AI technology, intelligent post-editing is gradually overcoming these limitations. By comparing models like GPT, Gemini, and Claude, the platform achieves precise correction of translation details throughout the entire document, significantly enhancing translation quality and user experience.
2. The Necessity of Post-Editing
Post-editing is a crucial step in ensuring translation quality. Currently, AI translation has reached near-human levels in capturing subtle contextual differences and most technical terms, but there may still be deviations in some proper nouns and unique expressions. This requires the use of terminology databases and post-editing to further correct and optimize the translated content.
In this article, we provide a detailed guide on how to perform manual post-editing: How to perform post-editing?
Currently, post-editing mainly relies on manual proofreading and modification. Translators usually compare the original text sentence by sentence to check whether the AI translation accurately conveys the original meaning, especially verifying easily misinterpreted proper nouns and industry terms. Although this method can effectively correct some issues, it often suffers from low efficiency, high costs, and significant influence from subjective judgment. Moreover, manual operations face certain difficulties in maintaining consistency and a unified style throughout the entire document.
3 The Application of AI Translation in Post-Editing
In post-editing, AI allows users to re-translate already translated sentences and compare different models to select the best translation. This intelligent translation feature has significant advantages over traditional AI translation, primarily in the following two aspects:
3.1 Comprehensive Application of the Entire Document Context
Traditional AI translation often focuses on translating individual sentences, whereas AI post-editing fully considers the context and structure of the entire document.
By conducting a comprehensive analysis of the context, AI can more accurately grasp the logical relationships and contextual information between sentences, thereby providing more natural and coherent translation processing, ensuring consistency in translation style and professional terminology.
3.2 Multi-Model Comparison to Select the Optimal Translation
O.Translator supports translation using various AI models such as GPT, Gemini, and Claude. Users can retranslate the same sentence using different models and compare the differences in semantic expression, technical terminology, and subtle contextual handling to select the best translation.
Comparing multiple models not only enhances translation accuracy but also gives users more control, making the translation better suited to actual needs.
4. Operation Process
4.1 Select the Sentence to be Edited
For sentences that may have translation omissions, the system provides a 'show untranslated' feature, which can filter out sentences in the document that have not been translated.
Users can directly use AI translation for these sentences.
Users can also select sentences that need retranslation or optimization for AI translation.

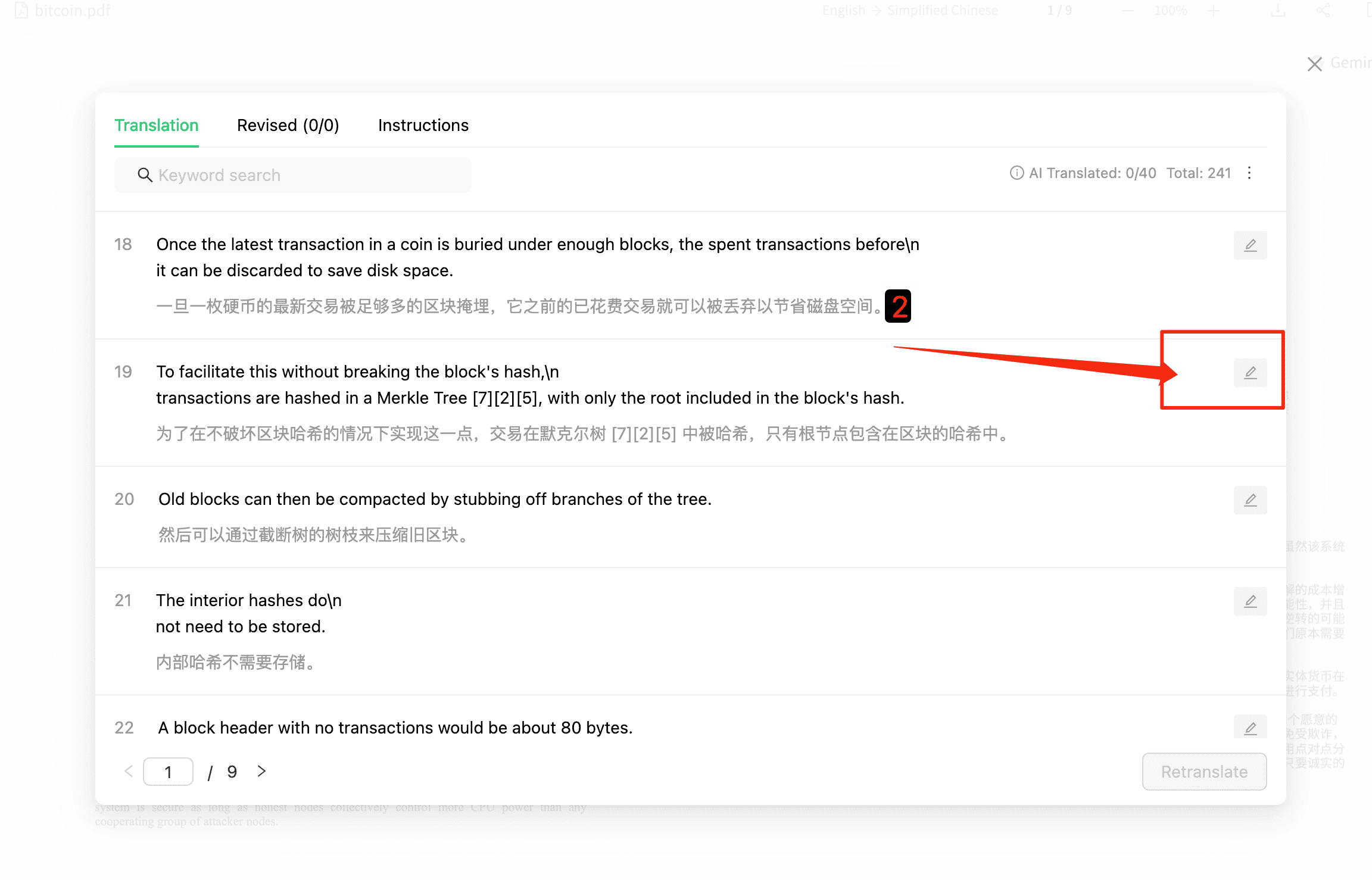
4.2 Choose Model for Re-Translation
The system automatically sends the sentence and its relevant context within the chapter to various AI models for translation, and once completed, it will automatically populate the input box.
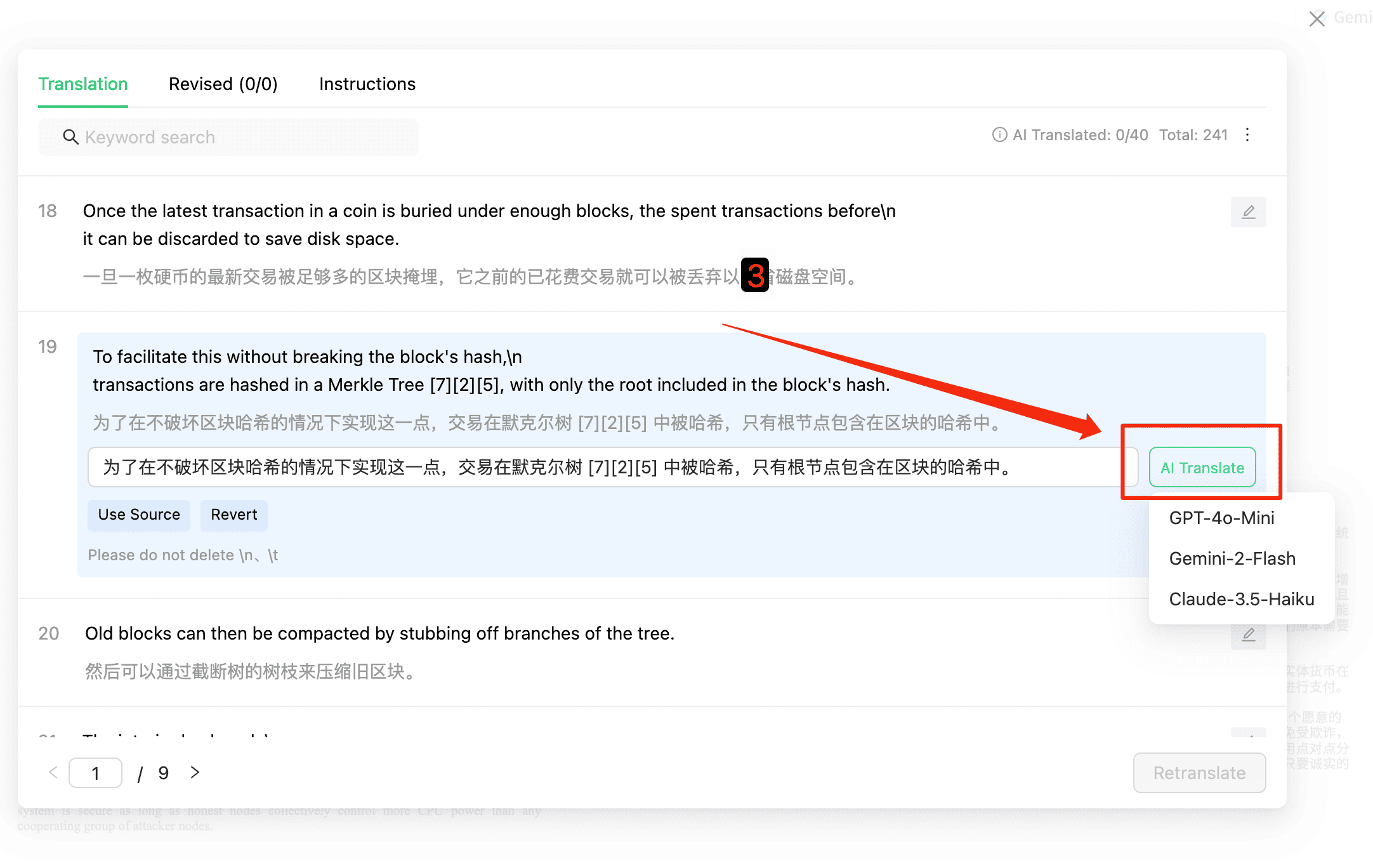
4.3 Comparison and Preview
Users can simultaneously view the results of the selected model's retranslation in the interface, allowing them to quickly compare and choose among previous translation results.
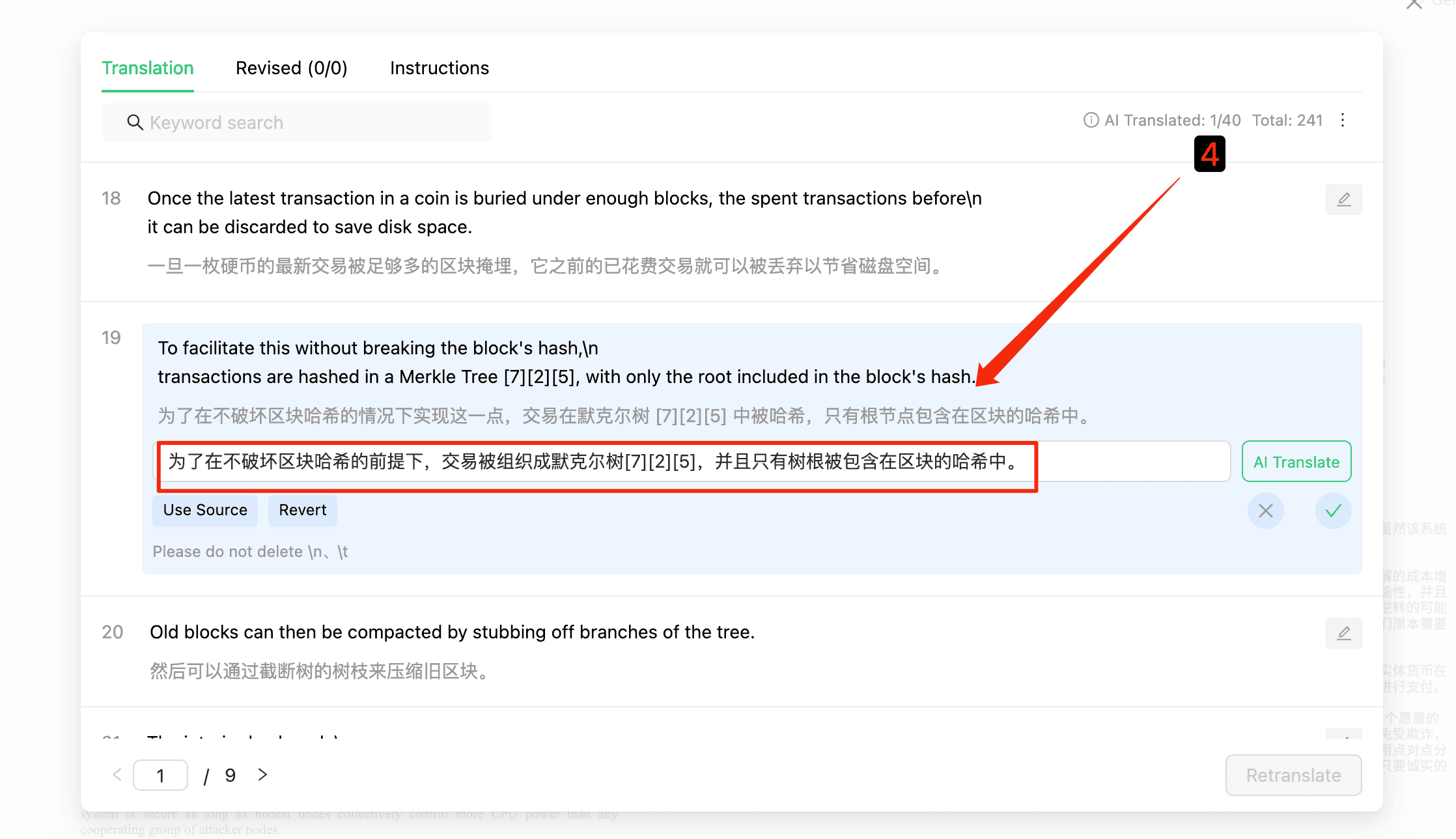
4.4 Multiple Translations and Save Draft
Users select the version that best meets their expectations for confirmation. After confirmation, the system saves this modification as a draft, which users can modify again and translate using AI.
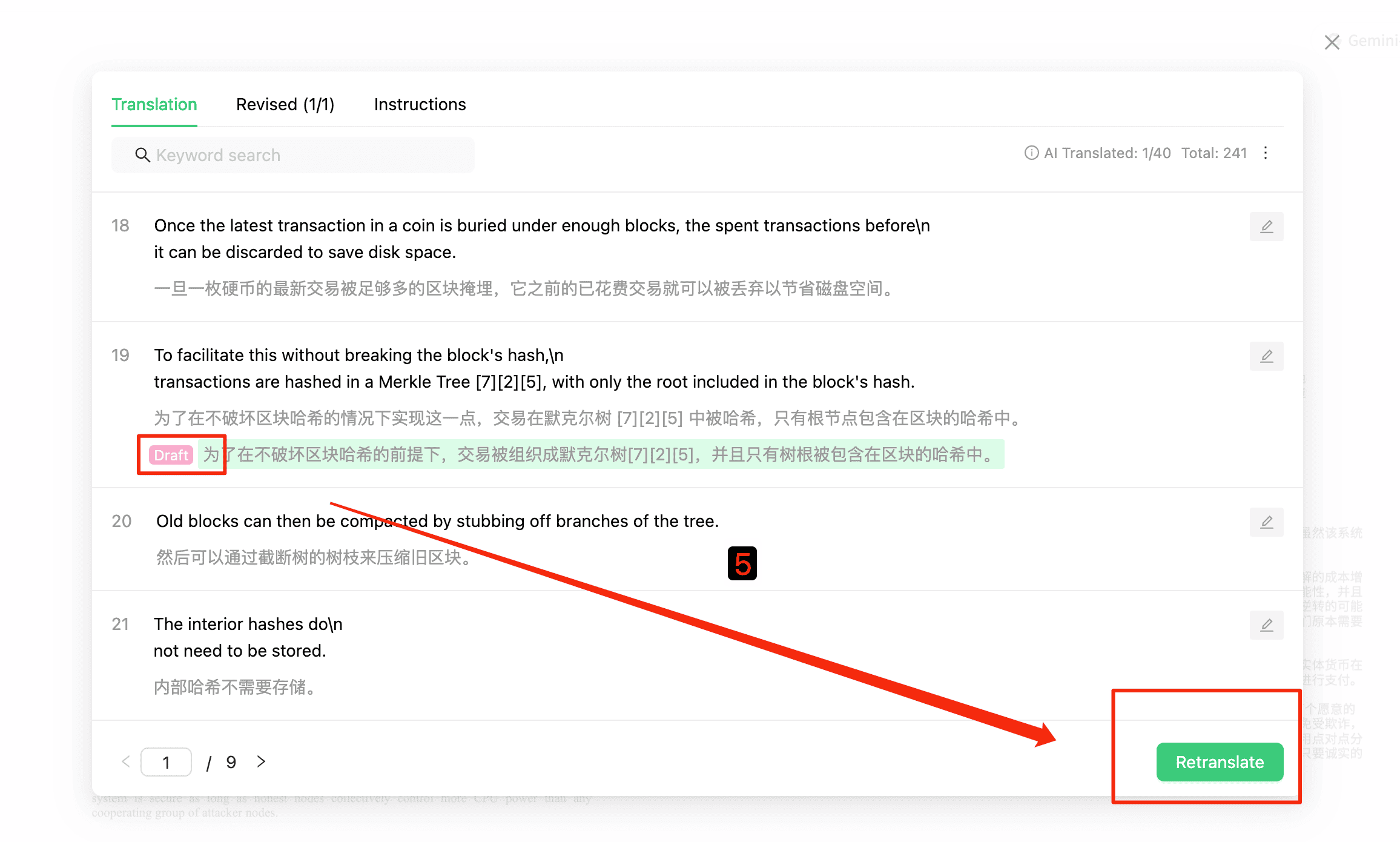
4.5 Confirm Re-Translation
Finally, users synchronize all edited drafts into the translation document through 'retranslation'.
5. Conclusion
In the future, we will do more to ensure the quality of document translation. We welcome you to try using O.Translator.
You can start exploring O.Translator with the Demo, try more Demos



